Have you ever wondered where you should store potentially hazardous food to ensure it remains safe for consumption? It’s a question that often lingers in the minds of anyone responsible for food storage. Potentially hazardous food must be stored in a designated refrigerator or cold storage unit. Storing potentially hazardous food properly is essential to maintaining food safety standards.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhen it comes to the storage of these types of foods, it is important to follow certain guidelines to prevent the growth of harmful bacteria and the risk of foodborne illnesses. One of the key steps in ensuring food safety is storing potentially hazardous food in the appropriate conditions.
This means that such foods should be stored in a designated refrigerator or cold storage unit, where the temperature is consistently maintained at or below 41°F (5°C). By adhering to proper storage practices, you can help protect the health and well-being of consumers and avoid potential legal and financial liabilities for your business.
Understanding Potentially Hazardous Foods
Potentially hazardous foods should be stored in designated areas that maintain the appropriate temperature to prevent foodborne illnesses. It is crucial to follow food safety guidelines to ensure that these foods are stored properly to minimize the risk of contamination.
Potentially hazardous foods are those that require specific conditions to be stored and handled to prevent the growth of harmful bacteria. These foods have a high moisture content and are typically perishable, making them susceptible to contamination and spoiling.
Understanding the definition and examples of potentially hazardous foods is crucial to maintaining food safety standards and protecting consumer health.

Definition And Examples Of Potentially Hazardous Foods
Potentially hazardous foods are those that provide an ideal environment for the growth of harmful bacteria, leading to foodborne illnesses. These foods require specific temperature control measures during storage and handling.
Examples:
- Meat (including poultry, pork, and beef)
- Fish and shellfish
- Dairy products (such as milk, cheese, and yogurt)
- Eggs and egg products
- Cut fruits and vegetables
- Cooked pasta and rice
- Soup, stock, and gravies
- Sauces and dressings containing dairy or eggs
Proper storage is crucial for potentially hazardous foods due to their perishable nature and potential to harbor harmful bacteria.
The following points explain why appropriate storage is essential:
Why Proper Storage Is Crucial For Potentially Hazardous Foods

Preserving Food Safety:
Maintaining safe storage conditions helps prevent the growth of harmful bacteria that cause foodborne illnesses. Adequate storage prevents cross-contamination, ensuring that potentially hazardous foods do not come into contact with other items that may contaminate them.
Preventing Spoilage:
Proper storage prevents the deterioration and spoilage of potentially hazardous foods, ensuring that they remain fresh and safe for consumption. Controlling temperature and humidity levels slows down the spoilage process, extending the shelf life of these perishable items.
Maintaining Quality and Taste:
By following appropriate storage practices, the quality, texture, and taste of potentially hazardous foods can be preserved. Correct temperature control and storage conditions help foods retain their flavor, color, and nutritional value, providing a better consumer experience.
Compliance with Food Safety Regulations:
Proper storage practices for potentially hazardous foods are not only essential for consumer safety but also comply with food safety regulations. Storing food correctly demonstrates a commitment to maintaining high standards of cleanliness and following proper food handling procedures.
Reducing Food Waste:
By storing potentially hazardous foods properly, food waste can be minimized. Correct storage conditions help prevent premature spoilage or product loss, leading to cost savings and a more sustainable approach to food management.
Remember, understanding the definition and examples of potentially hazardous foods is fundamental to ensuring food safety. Proper storage is crucial for preserving food quality, preventing spoilage, and complying with food safety regulations.
By following appropriate storage practices, both businesses and consumers can enjoy the benefits of fresh and safe food.
Factors To Consider When Storing Potentially Hazardous Foods
When storing potentially hazardous foods, it is important to consider proper temperature control, separation of raw and cooked foods, and adequate storage containers. Following these guidelines can help prevent foodborne illnesses and ensure the safety of your stored food.
Potentially hazardous foods require special attention when it comes to storage. By understanding and implementing proper storage practices, you can help ensure the safety and quality of the food you consume.
There are several key factors to consider when storing potentially hazardous foods, including temperature control requirements, the importance of monitoring and maintaining temperature levels, and the effects of improper temperature control on food safety.
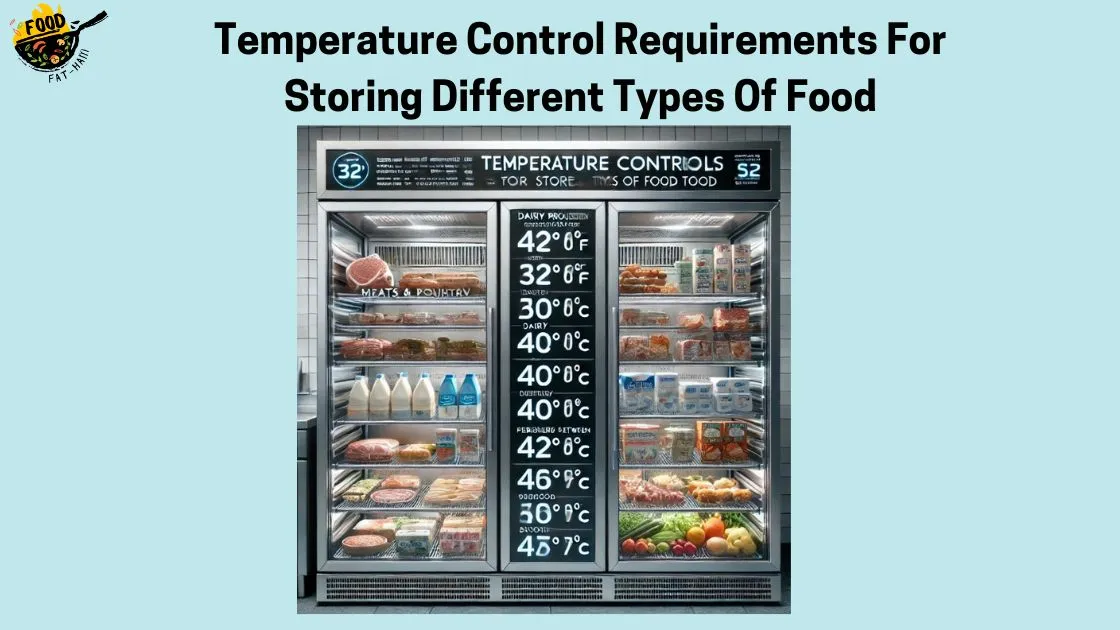
Temperature Control Requirements For Storing Different Types Of Food
- Meats and poultry: These should be stored at temperatures below 40°F (4°C) to prevent the growth of harmful bacteria.
- Dairy products: These should also be stored at temperatures below 40°F (4°C) to maintain their freshness and prevent spoilage.
- Seafood: Seafood should be stored at temperatures between 32°F (0°C) and 40°F (4°C) to ensure its quality and prevent the growth of bacteria.
- Perishable fruits and vegetables: These should be stored at temperatures between 32°F (0°C) and 45°F (7°C) to maintain their freshness and slow down the ripening process.
Importance Of Monitoring And Maintaining Temperature Levels
- By monitoring and maintaining proper temperature levels, you can prevent the growth of harmful bacteria that can cause foodborne illnesses.
- Proper temperature control also helps to maintain the taste, texture, and nutritional value of the stored food.
- It is crucial to regularly check and adjust the temperature of storage units to ensure they are within the recommended range.
Effects Of Improper Temperature Control On Food Safety
- Warm temperatures can accelerate the growth of bacteria, leading to potential foodborne illnesses.
- Cold temperatures that are too low can cause food to freeze, affecting its quality and texture.
- Fluctuating temperatures can cause bacteria to multiply rapidly, posing a significant risk to food safety.
By adhering to the temperature control requirements for different types of food, monitoring temperature levels consistently, and understanding the effects of improper temperature control, you can ensure the safety and quality of potentially hazardous foods. Implementing proper storage practices is essential for maintaining food safety and minimizing the risk of foodborne illnesses.
Remember to store your food at the appropriate temperatures to keep it fresh, nutritious, and free from harmful bacteria.
Recommended Storage Areas For Potentially Hazardous Foods
Potentially hazardous foods should be stored in designated areas to ensure safety. These storage areas must have proper temperature control, such as refrigeration or freezing, and should be separate from non-hazardous food items to prevent cross-contamination.
Refrigerated Storage: Maintaining Temperatures Between 32°F And 41°F
Set your refrigerator temperature within the safe range of 32°F to 41°F to prevent bacterial growth and keep your potentially hazardous foods fresh. Ensure that the refrigerator is functioning properly, regularly checking the temperature with a thermometer.
Place perishable items such as dairy products, raw meat, and seafood on the bottom shelves to avoid cross-contamination. Utilize refrigerator drawers designated for fruits and vegetables to maintain their freshness.
Freezer Storage: Maintaining Temperatures Below 0°F
- Keep your freezer temperature below 0°F to preserve the quality and safety of your potentially hazardous foods.
- Regularly monitor the temperature to ensure it remains in the ideal range for proper storage.
- Package foods properly to prevent freezer burn and maintain their texture and taste.
- Label and date all items in the freezer to track their freshness and prevent any potential hazards.
Dry Storage: Appropriate Conditions For Non-Perishable Foods
- Store non-perishable foods in a cool, dry, and well-ventilated area with a temperature below 85°F to extend their shelf life.
- Keep foods away from direct sunlight and humidity, as they can accelerate spoilage.
- Use airtight containers or packaging to protect foods from pests and maintain their quality.
- Regularly check for signs of spoilage, such as foul odors or mold, and discard any affected items promptly.
Dedicated Storage Areas For Raw And Cooked Foods
- Separate raw and cooked foods to prevent cross-contamination and reduce the risk of foodborne illnesses.
- Designate specific storage areas for raw and cooked foods, preferably using different shelves or zones in your refrigerator or pantry.
- Keep raw meats, poultry, and seafood securely wrapped to prevent any leaking or contact with other foods.
- Store cooked foods in covered containers or wrapped tightly to maintain their freshness and prevent any contamination.
Remember, following these recommendations for storing potentially hazardous foods will help ensure their safety and keep them at their best quality, providing peace of mind for you and your loved ones.
Importance Of Proper Packaging And Labeling
Proper packaging and labeling are crucial for storing potentially hazardous food. It ensures safety and reduces the risk of contamination, allowing for easy identification and proper handling of the food items.
Using Air-Tight Containers To Prevent Cross-Contamination And Spoilage
Air-tight containers play a vital role in ensuring the safety and quality of potentially hazardous food.
Here’s why:
- Air-tight containers create a barrier that prevents bacteria, viruses, and other contaminants from entering the food.
- The seal created by the container inhibits the growth of microorganisms, reducing the risk of foodborne illnesses.
- By eliminating exposure to air, the containers minimize oxidation and moisture loss, keeping the food fresh and flavorful for a longer time.
- These containers also help prevent the transfer of odors, flavors, and colors between different foods, avoiding cross-contamination.
- Make sure to choose air-tight containers made of food-grade materials, such as glass or high-quality plastic, for storing your potentially hazardous food items.
Labeling Food Items With Accurate Dates And Information
Proper labeling is crucial when it comes to storing potentially hazardous food.
Here’s why:
- Clearly labeling the food items helps you keep track of their freshness and enables you to practice the principle of first in, first out (FIFO) effectively.
- Include the date of purchase or preparation on the label to ensure you use the oldest items first, reducing the risk of spoilage.
- Additionally, labeling should provide information about the contents, ingredients, and any allergens present in the food, promoting food safety and awareness.
- Properly labeled food items also enhance organization and efficiency in the kitchen, preventing confusion and potential mistakes.
- Remember to use waterproof and smear-proof labels to ensure readability even in moist or refrigerated storage conditions.
Storage Guidelines For Packaged And Prepared Foods

Packaged and prepared foods require special attention when it comes to storage to maintain their safety and quality.
Here’s what you need to keep in mind:
- Store packaged foods according to the manufacturer’s instructions, as they often provide specific guidance on temperature, humidity, and shelf life.
- Keep raw and cooked foods separate to avoid cross-contamination, storing them in different areas or using separate containers.
- When it comes to prepared foods, cool them to the appropriate temperature before storing to prevent bacterial growth. Divide large portions into smaller portions for faster cooling.
- Refrigerate perishable prepared foods promptly to keep them within the safe temperature range, typically below 40°F (4°C).
- Regularly check the storage conditions, including the temperature of your refrigerator or freezer, to ensure they meet the recommended guidelines for safe food storage.
Remember, proper packaging and labeling are essential for maintaining the safety and quality of potentially hazardous food. Using air-tight containers helps prevent cross-contamination and spoilage, while accurate labeling ensures proper rotation and provides important information to promote food safety. Follow the storage guidelines for packaged and prepared foods to keep them fresh, delicious, and safe for consumption.
Organizing Your Storage Areas For Efficiency And Safety
Efficient and safe storage of potentially hazardous food is crucial. Follow these guidelines to organize your storage areas, ensuring proper labeling, temperature control, and separation from other food items to prevent contamination and promote food safety.
Shelf Organization Techniques For Easy Access And Rotation
- Categorize and label the different types of potentially hazardous foods. This will make it easier to locate specific items quickly.
- Store foods with the earliest expiration dates in the front and those with later dates behind them. This ensures that older items get used first, reducing the risk of spoilage or wastage.
- Consider using the FIFO (First In, First Out) method to ensure proper rotation of food items. It involves placing newly received items behind existing ones to ensure older stock gets used first.
- Keep heavier and bulkier items on lower shelves to prevent them from toppling over and causing accidents.
- Organize similar items together, such as meats, dairy, and vegetables, to make it easier to find what you need.
Separating Different Food Categories To Prevent Cross-Contamination
- Use separate shelves or storage areas for different food categories, such as raw meats, ready-to-eat foods, and produce.
- Ensure raw meats are stored on the lowest shelves to prevent any potential drips or spills from contaminating other foods.
- Use color-coded storage containers or labels to easily identify different food categories, reducing the risk of cross-contamination.
- Consider using dividers or separate containers within the same shelf to physically separate different types of foods.
- Regularly clean and sanitize the storage areas to prevent the buildup of germs and bacteria.
Best Practices For Reducing Food Waste And Maximizing Shelf Life:
Regularly inspect and remove any spoiled or expired food items to prevent contamination and maintain food quality.
Properly seal or wrap food items to prevent exposure to air, moisture, and pests, which can reduce shelf life.
Use clear storage containers to easily identify the contents and monitor the condition of the food.
Consider using a food inventory system to keep track of expiry dates and optimize stock levels.
Follow proper storage guidelines for temperature control and humidity to maximize the shelf life of different food items.
Remember, organizing your storage areas efficiently and ensuring food safety is vital in any kitchen environment. By implementing these techniques and practices, you can improve access and rotation, prevent cross-contamination, and reduce food waste.
Regular Monitoring And Maintenance
Regular monitoring and maintenance of potentially hazardous food requires proper storage to ensure safety. Store these foods at temperatures below 41°F or above 135°F to prevent bacterial growth and potential foodborne illnesses.
Importance Of Routine Temperature Checks And Equipment Calibration
Proper monitoring and maintenance of storage areas for potentially hazardous food is crucial for ensuring food safety and preventing the growth of harmful bacteria.
Here are the key reasons why routine temperature checks and equipment calibration should be a priority
Regular temperature checks:
Checking temperatures at regular intervals is essential to prevent bacterial growth and maintain the quality of perishable food items. Maintain cold storage temperatures at or below 40°F (4°C) to slow down bacterial growth, ensuring food safety. Regular temperature monitoring can help identify any refrigeration or cooling system malfunctions promptly, preventing potential food spoilage.
Equipment calibration:
Regularly calibrating thermometers and other temperature-measuring equipment ensures accurate readings, which are necessary for effective monitoring. Calibrate thermometers at least once a month to ensure they provide accurate temperature measurements and meet safety standards. Properly calibrated equipment guarantees that food is stored at the correct temperatures, reducing the risk of foodborne illnesses.
Guidelines For Proper Cleaning And Sanitization Of Storage Areas
Maintaining clean and sanitized storage areas is vital to prevent cross-contamination and the growth of harmful microorganisms. Follow these guidelines to ensure proper cleaning and sanitization:
- Regular cleaning:
- Clean storage areas frequently, removing any spills, debris, or food particles that can attract pests or promote bacterial growth.
- Use appropriate cleaning agents and sanitizers to eliminate harmful bacteria and viruses effectively.
- Pay special attention to high-touch surfaces such as shelves, racks, and handles, which are more prone to contamination.
- Sanitization process:
- Implement a regular sanitization process to eliminate any remaining germs after cleaning.
- Use sanitizing solutions approved by regulatory authorities to effectively kill bacteria, viruses, and other pathogens.
- Follow manufacturer instructions for proper dilution ratios and contact times to achieve efficient sanitization.
- Pest control:
- Implement pest control measures to prevent infestation and reduce the risk of contamination.
- Regularly inspect storage areas for signs of pests and take immediate action if any are found.
- Store food items off the ground and in tightly sealed containers to minimize pest access.
Implementing A Comprehensive Food Safety Plan
To ensure the overall safety of potentially hazardous food in storage areas, it is essential to establish a comprehensive food safety plan.
Consider the following key aspects when implementing a food safety plan:
Staff training and education:
Train all staff members on proper food handling, storage, and sanitation practices. Educate them about potential hazards, cross-contamination risks, and the importance of adhering to food safety protocols.
Documentation and record keeping:
Maintain detailed records of temperature checks, equipment calibration, cleaning, and sanitization schedules. Document any corrective actions taken in response to deviations from safety standards. Regularly review and update the food safety plan to incorporate any changes in regulations or best practices.
Regular audits and inspections:
Conduct regular audits and inspections to identify areas for improvement and ensure compliance with food safety regulations. Monitor storage areas, equipment performance, and staff practices to address any potential issues promptly.
Continuous improvement:
Encourage a culture of continuous improvement by seeking feedback from staff members and customers. Regularly review and update the food safety plan based on lessons learned and emerging best practices.
Adhering to these guidelines and implementing a comprehensive food safety plan will help ensure the proper storage of potentially hazardous food, minimizing the risk of foodborne illnesses and promoting overall food safety.
Training And Education For Food Handlers
To ensure the safety of potentially hazardous food, food handlers must store it in designated areas according to training and education standards. Proper storage facilities are essential in preventing contamination and maintaining food quality for consumption.
Ensuring Staff Members Understand The Importance Of Proper Food Storage
Conduct regular training sessions to educate all food handlers about the significance of correct food storage. Emphasize the potential risks associated with improper storage, including foodborne illnesses and customer dissatisfaction.
Promote awareness of the impact that mishandling food can have on the reputation and success of the establishment. Explain how proper storage helps maintain the quality, flavor, and safety of the food. Encourage questions and provide opportunities for open discussion to ensure staff members comprehend the importance.
Providing Training On Temperature Control, Labeling, And Organization
- Schedule comprehensive training on temperature control, covering the safe ranges for refrigeration, freezing, and cooking.
- Educate staff members about the appropriate methods of labeling packages, containers, and food items.
- Emphasize the importance of proper organization, including FIFO (first in, first out) rotation, to prevent spoilage and cross-contamination.
- Demonstrate correct techniques for taking and recording temperature readings to maintain food safety.
- Incorporate practical exercises to enable food handlers to gain hands-on experience and reinforce their understanding.
Regular Reinforcement Of Food Safety Protocols And Best Practices
Conduct regular follow-up sessions to reinforce food safety protocols and best practices. Provide feedback and guidance to ensure continuous improvement in staff performance. Share success stories and case studies related to proper food storage to motivate and inspire food handlers.
Update training materials to reflect new industry standards and emerging best practices. Encourage a culture of vigilance and accountability by recognizing and rewarding staff who consistently adhere to food safety protocols.
Remember:
- Staff members who understand the importance of proper food storage are more likely to diligently follow guidelines.
- Regular training and reinforcement sessions are essential to keep food handlers up to date with the latest industry standards and practices.
- Investing in training and education for food handlers is an investment in the reputation and success of your establishment.
Compliance With Food Safety Regulations And Standards
Storing potentially hazardous food correctly is crucial for compliance with food safety regulations and standards. It is important to designate specific areas that maintain the appropriate temperature control and prevent contamination, such as refrigerators, freezers, and dry storage spaces.
Familiarizing Yourself With Local Food Safety Regulations
- Understanding and complying with local food safety regulations is crucial for anyone handling potentially hazardous food.
- Familiarize yourself with the specific regulations and guidelines set by government authorities and health departments in your area.
- Ensure that you have a clear understanding of the requirements regarding the storage of potentially hazardous food to maintain food safety standards.
- Keep in mind that these regulations may vary from one jurisdiction to another, so thorough research is necessary to ensure compliance.
Meeting The Requirements Set By Government Authorities And Health Departments:
- Government authorities and health departments establish regulations and guidelines to safeguard public health and prevent foodborne illnesses.
- Adhering to these requirements is essential for food establishments to maintain their operating permits and licenses.
- Ensure that your storage practices meet the specified temperature, labeling, and handling requirements.
- Regularly inspect storage areas to verify compliance with regulations to minimize the risk of food contamination.
Keeping Up-To-Date With Any Changes Or Updates To Food Safety Standards:
- Food safety standards are subject to changes and updates based on evolving scientific knowledge and best practices.
- Stay informed about any revisions or new regulations introduced by government authorities or health departments.
- It is crucial to regularly review and update your knowledge regarding proper storage practices to ensure compliance with the latest food safety standards.
- Consider subscribing to industry newsletters or attending training sessions to stay up-to-date with any changes.
Remember, ensuring compliance with food safety regulations and standards is necessary to maintain the highest level of food safety. Familiarize yourself with local regulations, meet the requirements set by authorities, and stay informed about any updates or changes to ensure the safe storage of potentially hazardous food.
Frequently Asked Questions On Where Must You Store Potentially Hazardous Food
Where Must You Store Potentially Hazardous Food Quizlets?
Store potentially hazardous food in a safe and appropriate location.
Where Must You Store Potentially Hazardous Foods Dry Storage Break Room Cold Storage?
Potentially hazardous foods must be stored in dry storage, break room, or cold storage areas.
What Is The Safe Method Of Storing Potentially Hazardous Food?
Store potentially hazardous food safely by keeping it at the correct temperature and separating it from other foods.
How Potentially Hazardous Food Should Be Displayed?
Potentially hazardous food should be displayed following essential guidelines to ensure safety: 1. Keep potentially hazardous food separate from other foods. 2. Store at appropriate temperatures to prevent bacterial growth. 3. Use proper packaging and labeling to prevent cross-contamination. 4. Regularly monitor and document food temperatures to ensure food safety.
Conclusion
To ensure the safety of your customers and maintain food standards, storing potentially hazardous food correctly is essential. By following the proper guidelines, you can prevent contamination and the growth of harmful bacteria. Remember to always keep potentially hazardous food stored at the correct temperature, whether it is in the refrigerator, freezer, or hot holding area.
Regularly check and record the temperatures to guarantee the preservation and quality of the food. Additionally, utilize proper storage containers to prevent cross-contamination and label all food items clearly. Proper organization of your storage areas and regular cleaning are also crucial for maintaining a clean and safe environment.
By prioritizing the proper storage of potentially hazardous food, you can ensure the safety and satisfaction of your customers while fulfilling food safety regulations.



